The Frequency Theory of Hearing Would Best Be Described as
Amplitude spectrum describes the amplitude of each frequency component. It can be programmed to amplify only the frequencies you struggle to hear.

How Speakers Make Sound Animagraffs Loudspeaker Sound Audio Design
Inner ear contains the cochlea coiled tube which is filled with fluid and.
. It proposes that as pitch increases nerve impulses of the same frequency are sent to the auditory nerve. Their theories were known as telephone theories due to the similarity between the waveform of speech sound in a telephone line and the. The actual direct receptors for hearing are the a.
Two major theories that attempt to explain hearing are the frequency theory and place or resonance theory. Place theory is a theory of hearing which declares that our judgment of sound depends on where each element frequency generates oscillations along the basilar layer. The frequency theory was also called the telephone.
For those in the discipline of hearing one important application of the FFT is for the analysis of sound. This theory of how we hear sounds states that there are pulses that travel up the auditory nerve carrying the information about sound to the brain for processing and that the rate of this pulse matched the frequency of whatever tone you are hearing exactly. Proper citation formating styles of this definition for your bibliography.
Pages 17 This preview shows page 7 - 9 out of 17 pages. The description of the frequency components of sound. All of the options are correct.
Course Title PSYC 201. We thus hear the tone because the pulse traveling up the auditory. Now before you go pegging out all your EQs at 10 to 12k Hz to add airiness also understand that simply boosting this range wont give you anything but noise if nothing exists there to begin with.
The frequency theory of hearing is better than place theory at explaining our. This phenomenon is known as. The frequency of a wave is measured as the number of complete back-and-forth vibrations of a particle of the medium per unit of time.
The FFT has been described as the most important numerical algorithm of our lifetime. Sounds over 20 kHz are often too high for humans to hear and are typically referred to as ultrasound. The outer hair cells do an amplifying role and the detection of the sound and transmission to the brain via the auditory nerve is performed by the inner hair cells.
Frequency theory attempts to explain how the brain experiences sound waves. What is the frequency theory of hearing. Rinne 1865 and Rutherford 1880 proposed the early forms of the Frequency theory of hearing.
As the frequency of sound decreases so does our ability to detect and distinguish it. Temporal theory of hearing. A gestalt is best described as an a.
This is the idea behind the ________. It is important to assess the frequency distribution of the power in a sound because the human ear exercises that capacity in the hearing process. If a particle of air undergoes 1000 longitudinal vibrations in 2 seconds then the frequency of the wave would be 500 vibrations per second.
These frequencies can best be described as air That heady open quality to a sound usually results from good representation of overtones in this range. In general the higher the frequency of a sound wave the higher the pitch although wave amplitude also affects our perception of pitch. Frequency TheoryRutherford 1886 holds that pitch perception corresponds to the rate of vibration of.
See answer 1 Best Answer. Overall the human ear is best adapted to frequencies between 1000 and 3500Hz human speech covers the range of 200-8000Hz. Frequency theory of hearing.
Frequency organization of the cochlea. Volley theory states that groups of neurons of the auditory system respond to a sound by firing action potentials slightly out of phase with one another so that when combined a greater frequency of sound can be encoded and sent to the brain to be analyzed. The frequency theory of hearing is better than place.
Between 20 and 200 hertz is known as low-frequency sound and anything below is known as infrasound 2. Tympanic theory of hearing. A complex sound that contains all frequency components and whose instantaneous amplitude varies randomly.
According to the frequency theory the pulse rate of the nerve vibrations of the hearing nerve communicates to the rate of a pitch which enables us to identify its pitch. Typically the best type of hearing aid for high-frequency hearing loss is whats known as a receiver-in-the-ear RITE with a dome that sits in the ear canal. Before frequency theory can be fully.
Place theory of hearing. If we see a speaker mouthing day while actually hearing someone else saying may we may perceive a third syllable bay that blends both inputs. The theory was proposed by Ernest Wever and Charles Bray in 1930 as a supplement to the frequency theory.
Frequency theory of hearing suggests that the entire basilar membrane acts like microphone vibrating as a whole in response to a sound. Low-frequency sounds are perceived as lower pitch due to activation of cilia deep in the cochlea whereas high-frequency sounds are higher pitched and processed closer to the base of the cochlea. Phase spectrum describes the phase of each frequency component.
Depending on your gender age and occupation each persons audible range may fluctuate but usually it is within those limits. The wavelengthof sound is described in terms of frequencyas measured in cycles per second or Hertz. When you hear a tone of 200 Hz the hair cells in the cochlea begin vibrating 200 times per second.
This style has an open fit so it doesnt muffle the low-frequency sounds that you still hear naturally. While frequency theory is primarily a physiological theory that seeks to explain how the anatomical structure of the ear accounts for hearing it is also a psychological theory that explores how sound is experienced by the mind. A commonly used unit for frequency is the Hertz abbreviated Hz where.
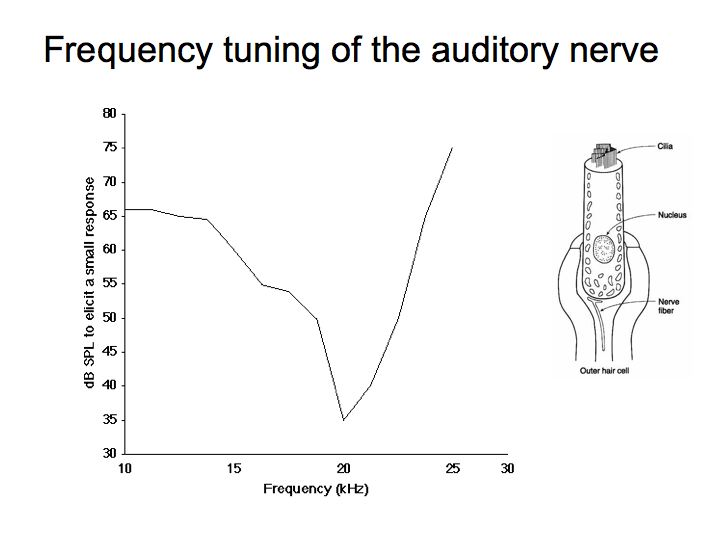
Perception Lecture Notes Frequency Tuning And Pitch Perception
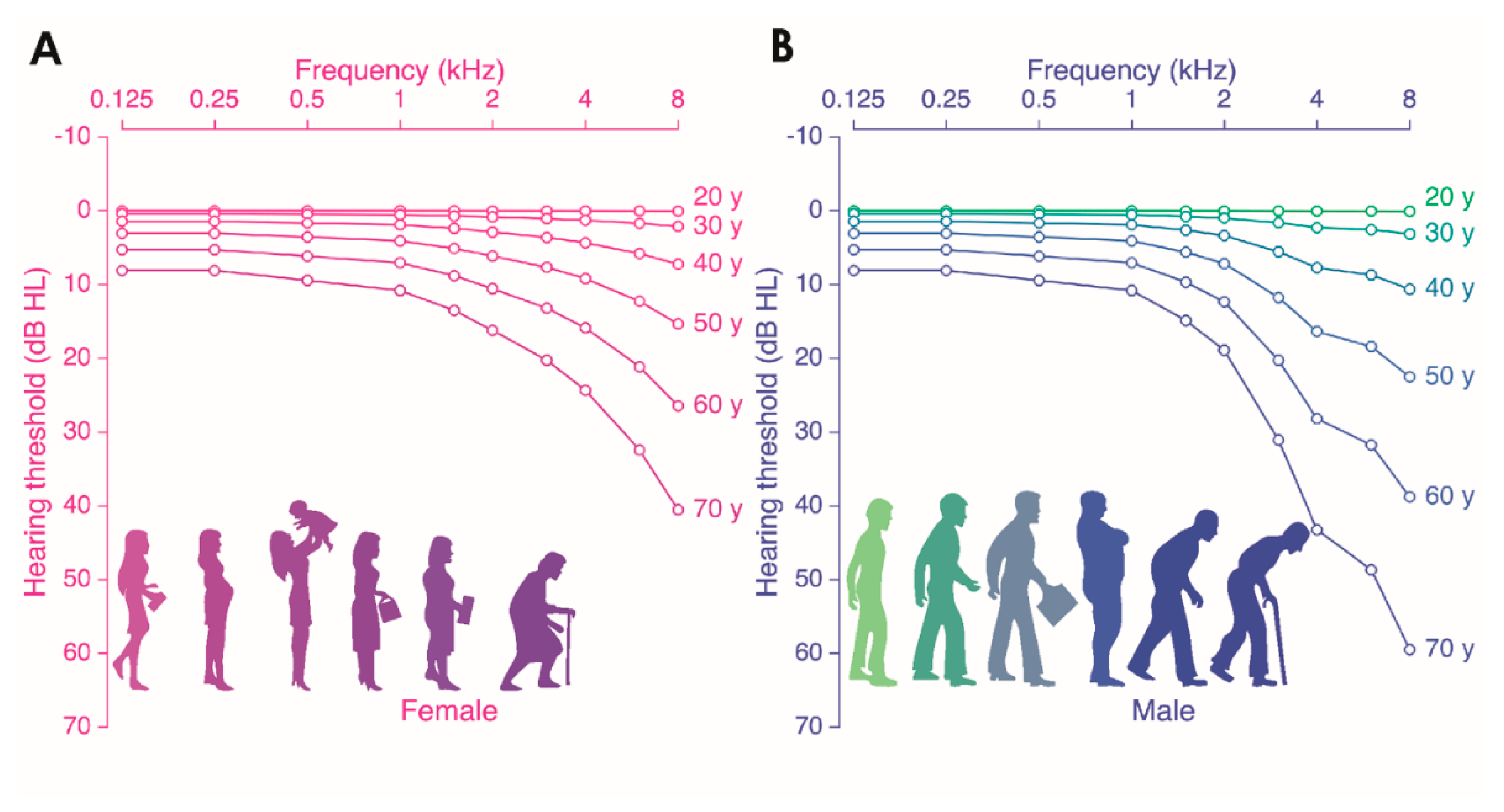
Jcm Free Full Text Presbycusis An Update On Cochlear Mechanisms And Therapies Html

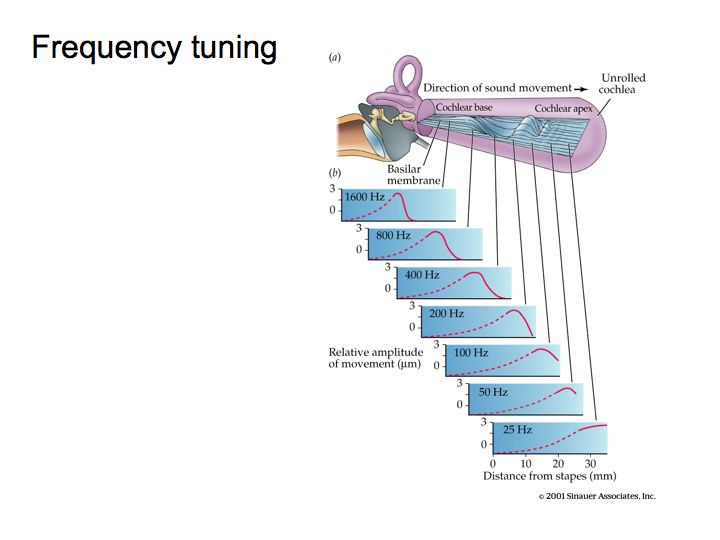
Perception Lecture Notes Frequency Tuning And Pitch Perception

The Effects Of Age Related Hearing Loss On The Brain And Cognitive Function Trends In Neurosciences
Comments
Post a Comment